git 基础知识与使用
Git
本文内容基于 The Missing Semester of Your CS Education - 版本控制(Git) 改编
Git 相关学习资料看这里
一、理论知识
版本控制系统 (VCSs)
- Version Control Systems
- 用于追踪源代码(或其他文件、文件夹)改动的工具
- 管理代码的修改历史
- 让协作编码变得更方便
- VCS
- 通过一系列的快照将某个文件夹及其内容保存了起来
- 每个快照都包含了文件或文件夹的完整状态
- 同时它还维护了快照创建者的信息以及每个快照的相关信息
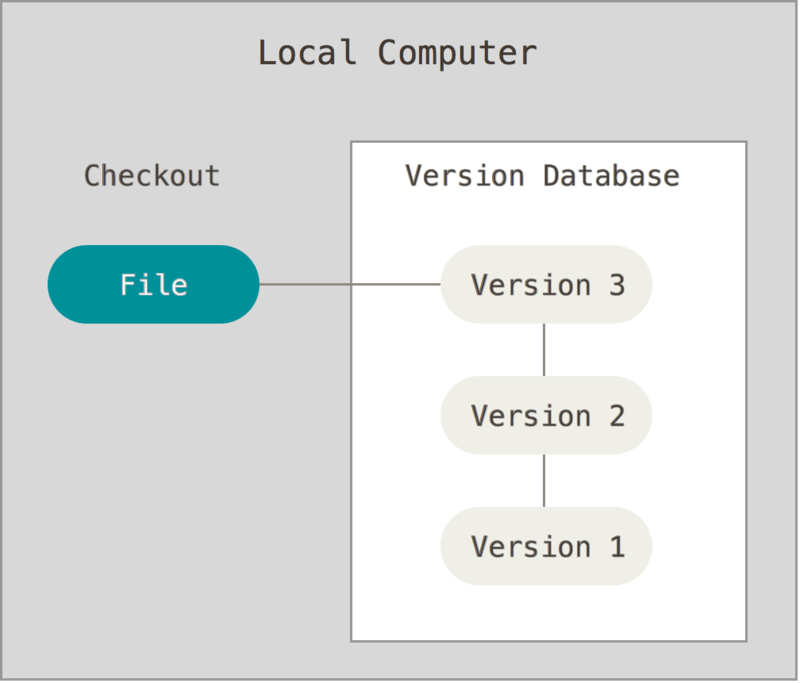
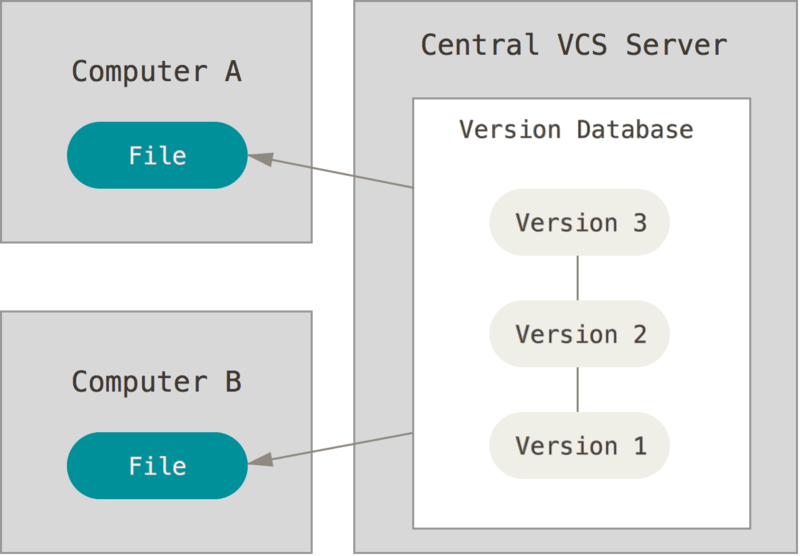
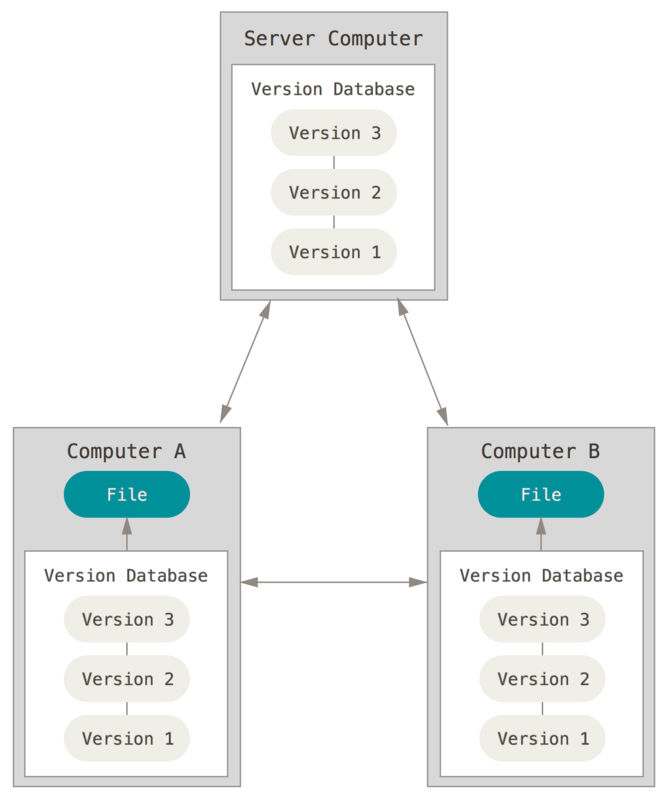
Git
直接记录快照,而非差异比较
Wikipedia :Git (/ɡɪt/) is free and open source software for distributed version control
- 很多时候只能死记硬背一些命令行,然后像使用魔法一样使用它们。
- 一旦出现问题,就只能像这幅漫画里说的那样去处理了😅
- 毕竟只知道硬背命令,不知道所处的情况,遇到报错最简单的处理方式莫过于保存现在的工作,然后删掉混乱的仓库,重新克隆仓库,再粘回去
- 一旦出现问题,就只能像这幅漫画里说的那样去处理了😅

Git 的数据模型
快照
- Git 将顶级目录中的文件和文件夹作为集合,并通过一系列快照来管理其历史记录。
- 文件被称作Blob对象(数据对象),也就是一组数据。
- 目录则被称之为 tree,它将名字与 Blob 对象或树对象进行映射(使得目录中可以包含其他目录)。
- 快照则是被追踪的最顶层的树。
1 | <root> (tree) |
历史记录建模:关联快照
- 有向无环图
- Git 中的每个快照都有一系列的“父辈”,也就是其之前的一系列快照。
- 注意,快照具有多个“父辈”而非一个,因为某个快照可能由多个父辈而来。
- 例如,经过合并后的两条分支。
可视化展示一下:
1 | o <-- o <-- o <-- o |
- o 表示一次提交(快照)
- 箭头指向当前提交的父辈
- 第三次提交之后,历史记录分岔成了两条独立的分支
- 可能因为此时需要同时开发两个不同的特性,他们之间是相互独立的
1 | o <-- o <-- o <-- o <---- o |
- 开发完成后,这些分支可能会被合并并创建一个新的提交,这个新的提交会同时包含这些特性。
数据模型的伪代码表示
1 | // 文件就是一组数据 |
对象和内存寻址
1 | // Git 中的对象可以是 blob、tree、commit |
例如上面例子中的树:
1 | 698281bc680d1995c5f4caaf3359721a5a58d48d 是顶层树的哈希值 |
引用
- 所有的快照可通过哈希值标记,但是40位的16进制字符串难以记忆
- 给这些哈希值赋予人类可读的名字,也就是引用(references)
- 引用是指向提交的指针
- 引用可以被更新,指向新的提交
- master 引用通常会指向主分支的最新一次提交
- 当前的位置有一个特殊的索引: “HEAD”
1 | references = map<string, string> |
仓库
- 粗略的Git仓库定义:对象 和 引用
- 在硬盘上,Git 仅存储对象和引用
版本库、工作区、暂存区
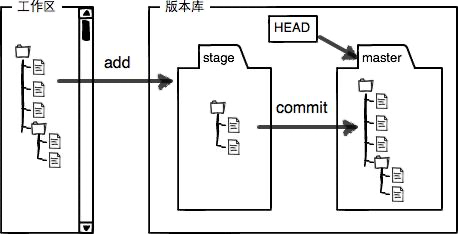
我们把文件往Git版本库里添加的时候,是分两步执行的:
- 第一步是用
git add把文件添加进去,实际上就是把文件修改添加到暂存区; - 第二步是用
git commit提交更改,实际上就是把暂存区的所有内容提交到当前分支。
协议
- 本地协议(Local protocol): 其中的远程版本库就是同一主机上的另一个目录。
git clone /srv/git/project.git
- HTTP 协议:
git clone https://github.com/git/git.git
- SSH 协议:
git clone ssh://[user@]server/project.git
- Git 协议:
git clone git@github.com:git/git.git
📌 Remove my password from list so hackers won't be able to hack me
Remove my password from list so hackers won't be able to hack me
二、基本操作
- 下载: https://git-scm.com/
- 安装:官方安装帮助文档
基础命令
1 | git --version |
git config 相关
git config 相关- 通过
git config --local进行的配置将保存在当前 git 仓库的.git/config文件中 - 通过
git config --global进行的配置将保存在当前用户家目录的.gitconfig文件中
第一次提交
1 | cd /tmp |
创建一个分支
1 | git switch -c dev |
📌 关于 git checkout 与 git switch 和 git restore
git checkout 与 git switch 和 git restoregit checkout 这个命令既被用来切换分支,又被用来恢复工作区文件,对用户的认知造成了较大的困惑。Git自2.23版本开始引入两个新的命令: git switch 和 git restore,用来替代 git checkout
git switch: 负责分支管理git switch <branch_name>切换至指定分支git switch -c <branch_name>创建新的分支并切换至该分支
git restore: 负责文件恢复
合并分支
1 | 正常合并不出错的情况: |
查看差异
1 | echo checkofdiff > baz.txt |
回退
1 | 尚未添加到暂存区时 |
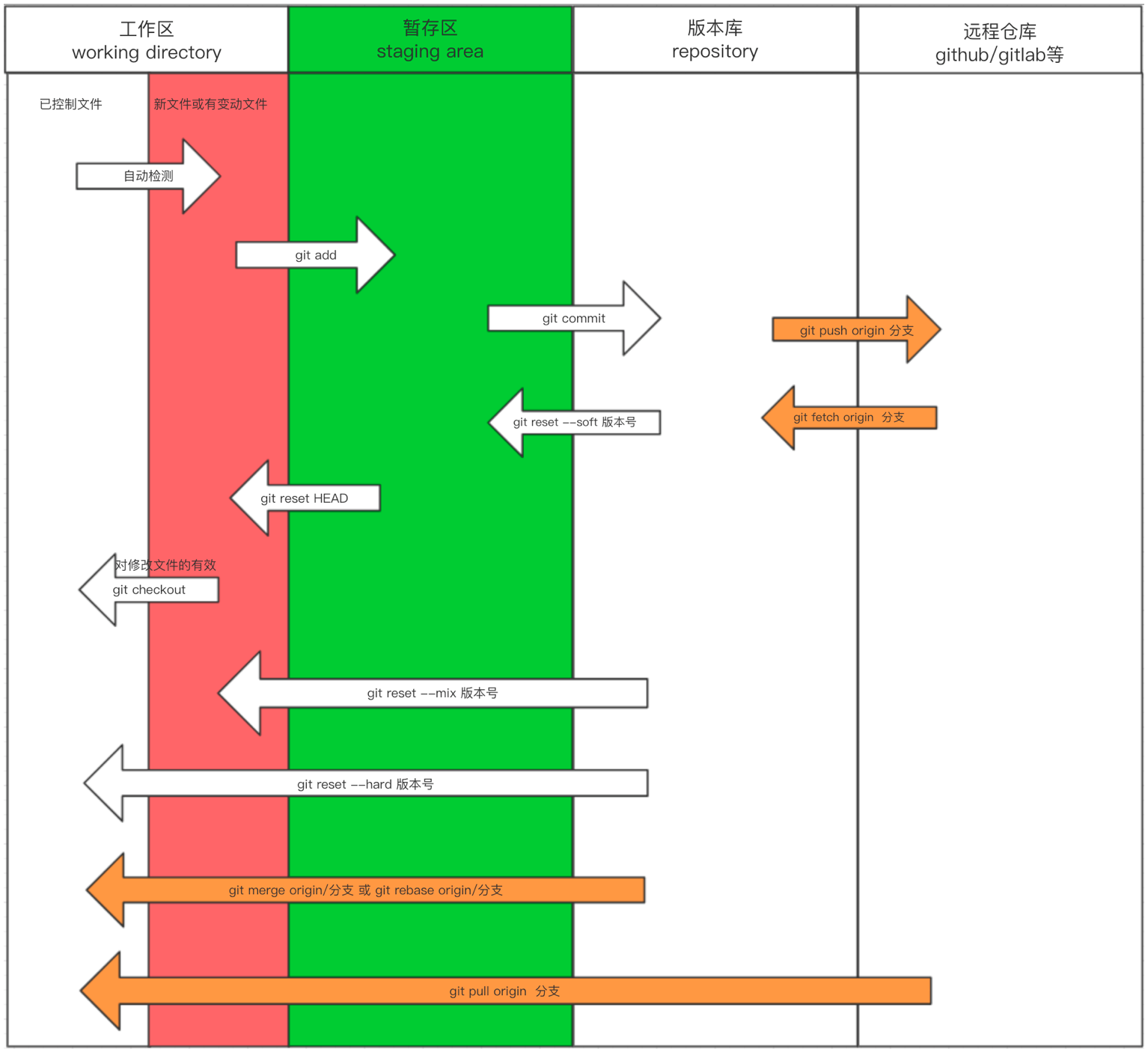
远程仓库
1 | git remote add origin git@github.com:ex7l0it/git_learning.git |
Github相关
- 配置 SSH Key: https://github.com/settings/keys
- 可通过 SSH 协议进行身份认证,进行 clone、push 等操作
- 生成 Personal Access Tokens 👉 https://github.com/settings/tokens
- 推荐使用新出的细粒度的 Personal Access Token 👉 https://github.com/settings/personal-access-tokens/
- 可针对指定仓库进行细粒度的配置
- 可通过 HTTPS 协议进行身份认证
- 推荐使用新出的细粒度的 Personal Access Token 👉 https://github.com/settings/personal-access-tokens/
三、更多命令及应用场景
1. 当你已经更改了很多内容,突然发现需要把修改的内容移动到新分支
- 解决方案:使用
git stash进行暂存工作
1 | git stash # 保存当前工作区修改的内容 |
git stash 相关命令:
1 | 保存工作现场 |